Not ready for a baby but still want to enjoy sex? I got you. Contraception (birth control) allows individuals to decide if and when to have children by preventing or delaying pregnancy. Discover the most effective methods to prevent pregnancy, including hormonal, barrier, natural, and permanent options. This comprehensive guide includes clear explanations, images, and trusted links to help you make informed choices about contraception.
Here are 5 major and reliable methods and types to prevent pregnancy—no myths, no superstitions, just proven facts.
Table of Contents
Hormonal Methods
Birth Control Pills: These are daily pills containing hormones (estrogen and progestin, or progestin only). They work by preventing the ovaries from releasing an egg (ovulation) each month, and by thickening cervical mucus and thinning the uterine lining so sperm cannot reach an egg.

Birth control pills are one of the most common contraceptives. When taken daily and at the same time, they are 99% effective at preventing pregnancy. The pill contains hormones that prevent ovulation, so there’s no egg for sperm to fertilize.
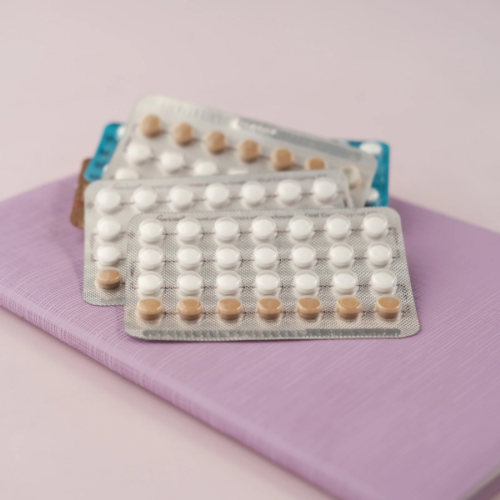
Where to get it? Any pharmacy around you. Just ask the pharmacist.
Implant: A small rod (about the size of a matchstick) is inserted under the skin of the upper arm. It steadily releases progestin for several years. Progestin pauses ovulation (no egg is released) and thickens cervical mucus, making it hard for sperm to reach any egg.
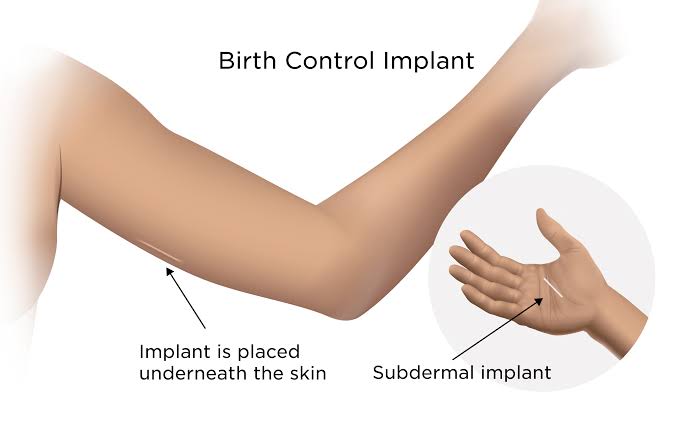
This small, flexible rod is inserted under the skin of your upper arm and prevents pregnancy for up to 3 to 5 years. It works by releasing hormones that stop ovulation and make it hard for sperm to reach the egg.
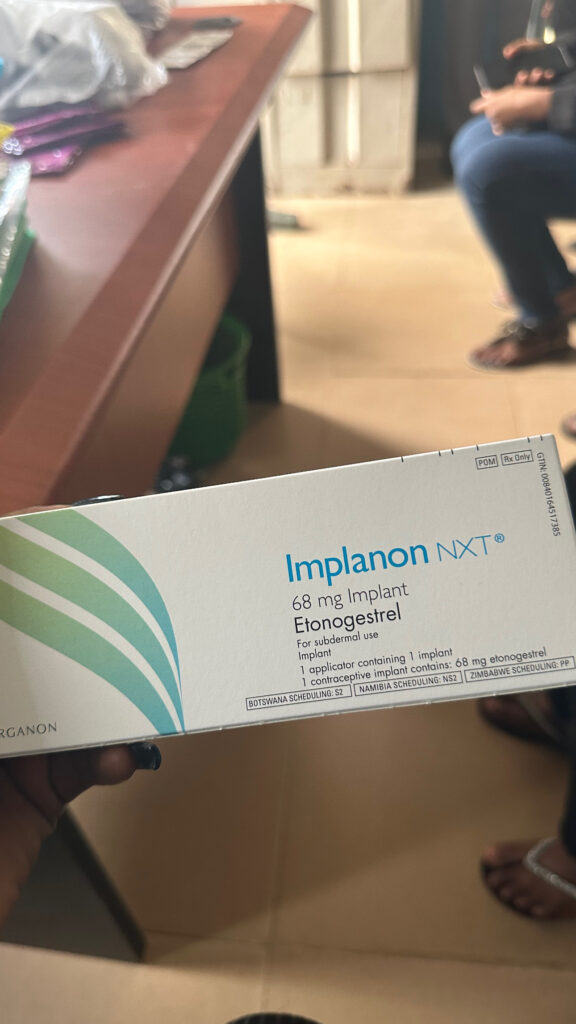

Where to get it? Government hospitals, family planning clinics, and private hospitals.
Injectable Contraceptives (Shot): A person receives an injection of progestin (e.g. Depo-Provera) every 3 months. Like the implant, the progestin shot stops ovulation and thickens cervical mucus so sperm cannot reach an egg.
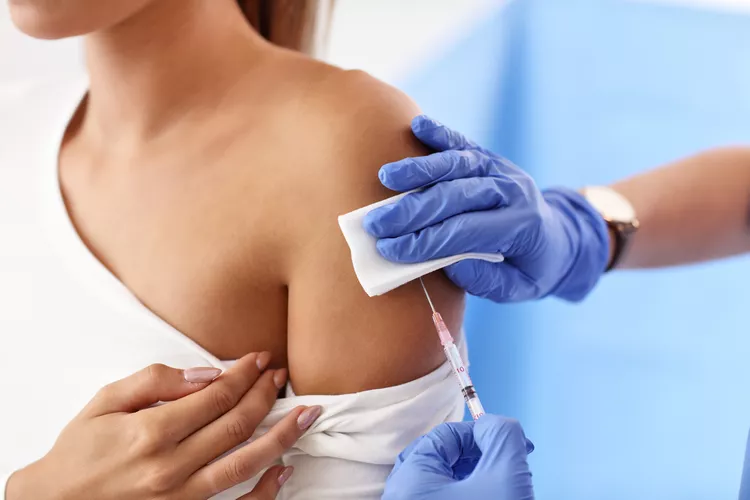
This is an injection you take every three months to prevent pregnancy. It stops ovulation and thickens cervical mucus to block sperm. If you hate remembering pills daily, this might be for you.
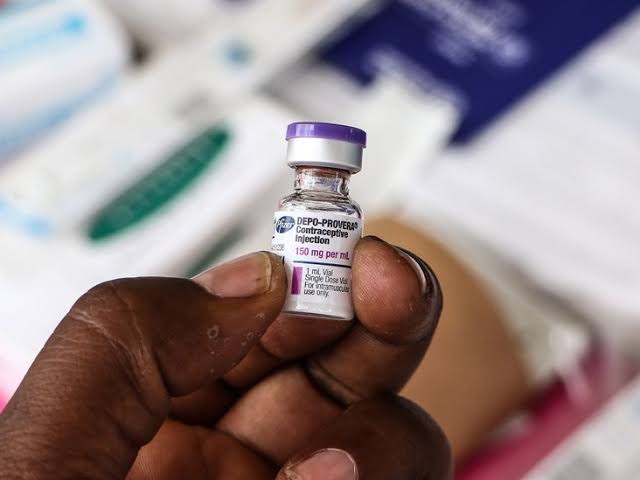
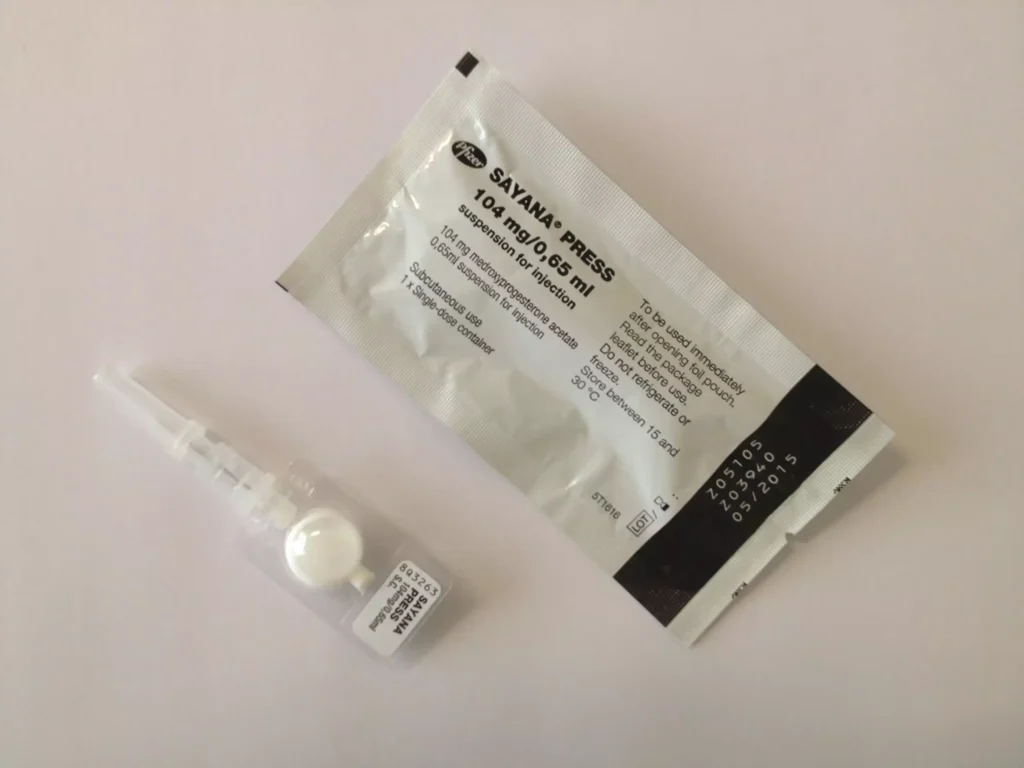
Where to get it? Family planning clinics, pharmacies, and hospitals.
IUD (Intrauterine Device): A T-shaped device placed into the uterus. There are two main types: a hormonal IUD (e.g. Mirena) releases progestin, which thickens cervical mucus and partially suppresses ovulation, and thins the uterine lining; a copper IUD releases copper ions that create an environment toxic to sperm. Copper IUDs stop fertilization by preventing the sperm and egg from uniting and by altering the uterine environment. Both types prevent pregnancy for several years.
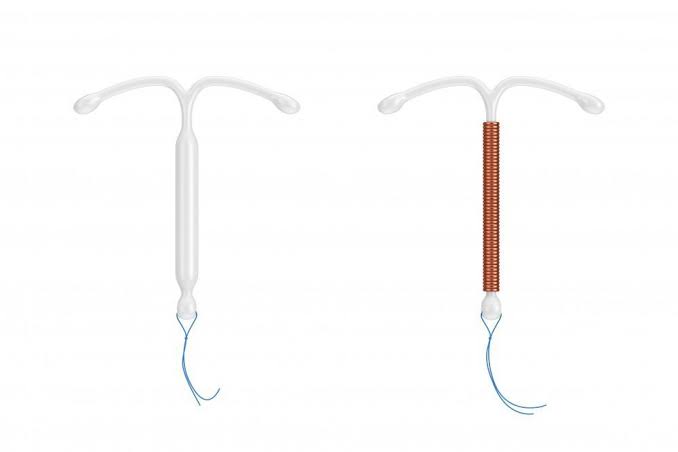
An IUD is a small device inserted into the uterus by a doctor. There are two types:
Copper IUD (e.g., Pregna) – prevents pregnancy for up to 10 years.

Hormonal IUD (e.g., Mirena) – lasts 3 to 5 years and reduces menstrual cramps

Once inserted, you don’t have to do anything—it works on its own..
Where to get it? Family planning clinics and hospitals.
Vaginal Ring: A flexible hormonal ring (e.g. NuvaRing) is inserted into the vagina for three weeks each month. It releases estrogen and progestin directly through the vaginal wall. These hormones stop ovulation so no egg is released, and also thicken cervical mucus to block sperm.
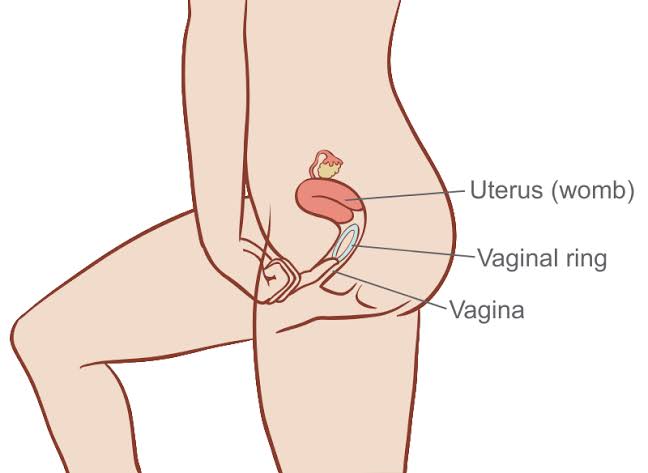
This is a small flexible ring inserted into the vagina that releases hormones to prevent ovulation. It stays in for three weeks, then you remove it for a week before inserting a new one. It is 91 to 99 percent effective when used correctly.
Where to get it? Not very common in Nigeria, but some big pharmacies and private hospitals might have it.
Barrier Methods
Condoms: Male (external) and female (internal) condoms create a physical barrier that keeps sperm from entering the uterus. Latex condoms are widely used; they are the only contraceptive method that also provides protection against HIV and other STIs. By physically blocking sperm, condoms prevent fertilization.

When used correctly, male condoms are 98% effective,

while female condoms are about 95% effective.

Always check for tears or expiration dates before use. Do not keep them in your wallet or car for too long because heat can damage them.
Where to get it? Any pharmacy around you, just ask the pharmacist.
Emergency Contraception Pills (Postinor, Postpill, Backup)
Emergency Contraceptive Pills: Often called the “morning-after pill,” these high-dose hormone pills (e.g. Plan B One-Step or ella) are taken within days after unprotected sex. They work primarily by delaying or preventing ovulation so that no egg is available to be fertilized. For best effect, they should be taken as soon as possible (ideally within 72 hours). A copper IUD can also be used as emergency contraception if inserted within about 5 days of unprotected sex, preventing pregnancy by stopping fertilization. (Note: emergency methods do not terminate an existing pregnancy.)
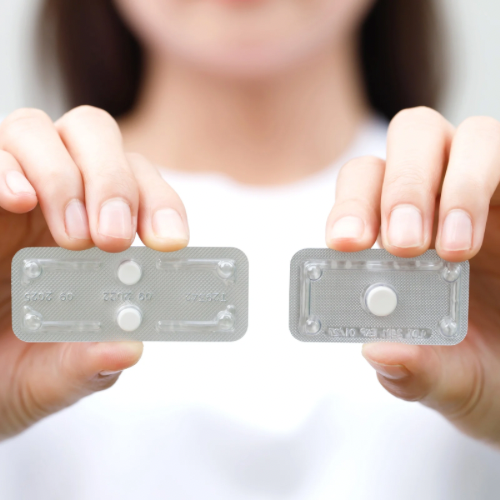

If you had unprotected sex or a condom broke, you can take an emergency contraceptive pill within 72 hours to prevent pregnancy. However, this is not a regular birth control method and should only be used in emergencies.
Where to get it? Any pharmacy near you.
Natural Methods
Withdrawal (Pull-Out Method): The man withdraws his penis from the vagina before ejaculation so that sperm are released outside the body. The goal is to prevent sperm from entering the vagina. This method requires careful timing and does not protect against STIs.
While it can work, it’s risky because pre-cum may contain sperm. If your partner isn’t quick or disciplined enough, it could fail. Use this with condoms or other birth control methods for extra protection.
The pull-out method is about 78% effective. About one in five people who rely on the pull-out method for birth control become pregnant.
Fertility Awareness (Natural Family Planning): The woman tracks menstrual cycle indicators (calendar days, basal body temperature, cervical mucus changes, etc.) to identify fertile days. Couples then avoid unprotected sex (or use a barrier) during the fertile window each cycle. By not having intercourse on days with an egg available, pregnancy is prevented. This method requires regular cycles and discipline.

This involves tracking your menstrual cycle to know your fertile and non-fertile days. If you have regular cycles, you can avoid sex or use protection on your fertile days.
How to track it?
Use apps like FLO, Clue, or Period Tracker
Be consistent—one mistake and you could end up shopping for baby clothes.
Permanent Birth Control (Tubal Ligation or Vasectomy)
If you’re completely sure you don’t want kids, there are permanent solutions:
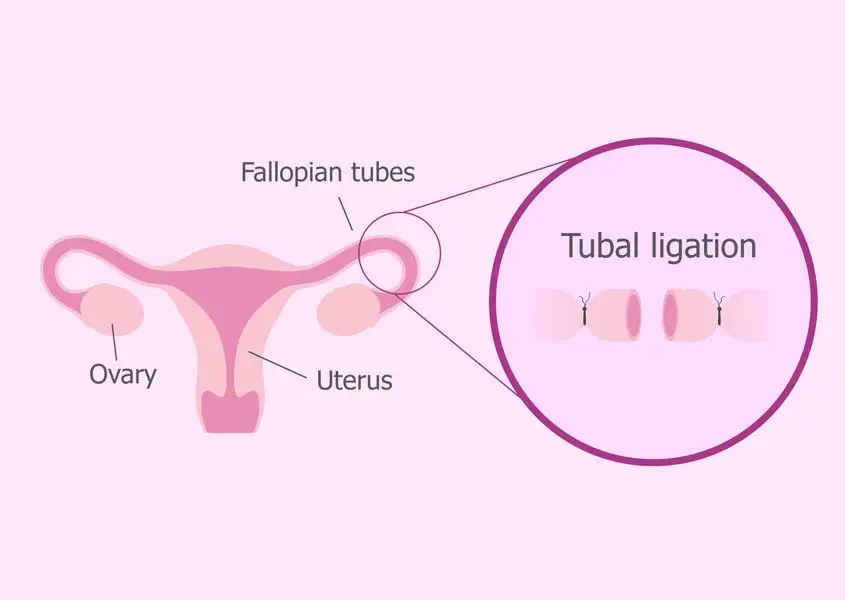
Tubal Ligation (Female Sterilization): A surgical procedure (often called “having your tubes tied”) where the fallopian tubes are cut, tied, or sealed. This permanently blocks eggs from traveling from the ovaries to the uterus and prevents sperm from reaching any egg. Once healed, it immediately prevents pregnancy (failure rate ~0.5%). Tubal ligation is intended as lifelong birth control..
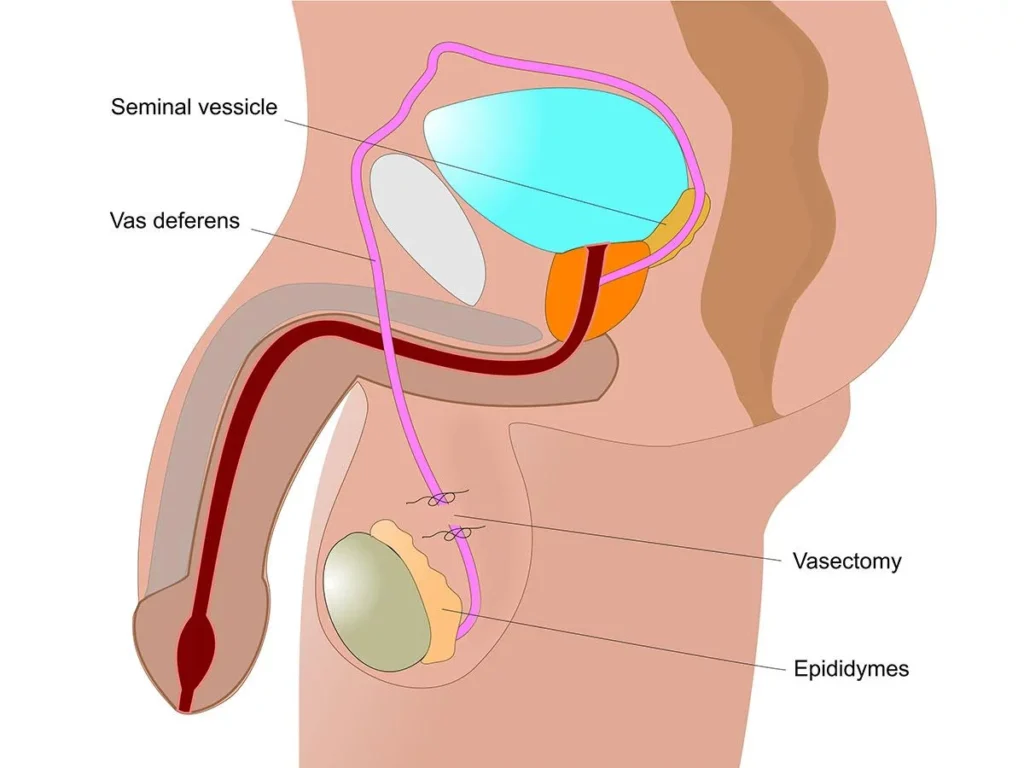
Vasectomy (Male Sterilization): A minor surgical procedure for men. The surgeon cuts and seals each vas deferens (the tubes carrying sperm). After vasectomy, the penis continues to ejaculate semen, but it contains no sperm. This nearly 100% effective surgery is also meant to be permanent (though sometimes reversible), and it has a very short recovery time.
This method is irreversible, so think it through before choosing it.
No matter your lifestyle, there’s a birth control method that works for you. Some are hormonal, some are non-hormonal, and others are permanent. If you’re unsure which is best for you, visit a family planning clinic or speak to a doctor.
Enhancing pleasure is great, but combining it with safety, like using contraceptives, is even better. Check out our guide on erogenous zones to level up your intimacy safely.
And remember, ONLY condoms protect against pregnancy and STIs!
Which method have you tried or are you considering? Drop a comment


Leave a Reply